Post by Super Communist on Dec 12, 2011 21:34:28 GMT -5
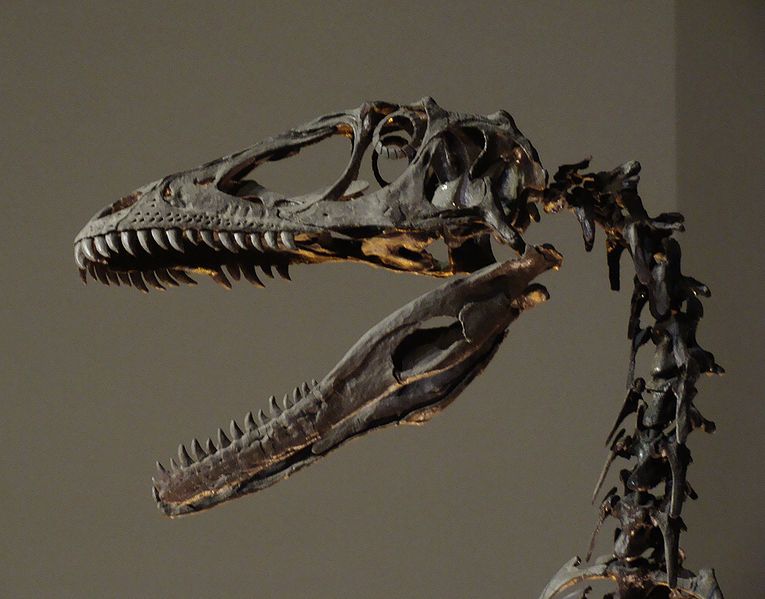
Based on the largest known specimens, Deinonychus could reach at least 3.4 metres (11 ft 2 in) in length, with a skull length of 410 mm (16.1 in), a hip height of 0.87 metres (2 ft 10 in), and an estimated weight of 73 kilograms (160 lb). Its skull was equipped with powerful jaws lined with around seventy curved, blade-like teeth. Studies of the skull have progressed a great deal over the decades. Ostrom reconstructed the partial, imperfectly preserved, skulls that he had as triangular, broad, and fairly similar to Allosaurus. Additional Deinonychus skull material and closely related species found with good three-dimensional preservation show that the palate was more vaulted than Ostrom thought, making the snout far narrower, while the jugals flared broadly, giving greater stereoscopic vision. The skull of Deinonychus was different from that of Velociraptor, however, in that it had a more robust skull roof like that of Dromaeosaurus, and did not have the depressed nasals of Velociraptor. Both the skull and the lower jaw had fenestrae (skull openings) which reduced the weight of the skull. In Deinonychus, the antorbital fenestra, a skull opening between the eye and nostril, was particularly large.
Deinonychus possessed large hands (manus) with three claws on each forelimb. The first digit was shortest and the second was longest. Each hind foot bore a sickle-shaped claw on the second digit, which was probably used during predation.
No feathers have ever been found in association with fossils of Deinonychus. Nonetheless, the evidence suggests that the Dromaeosauridae, including Deinonychus, had feathers. The genus Microraptor is both older geologically and more primitive phylogenetically than Deinonychus, and within the same family. Multiple fossils of Microraptor preserve pennaceous, vaned feathers like those of modern birds on the arms, legs, and tail, along with covert and contour feathers. Velociraptor is geologically younger than Deinonychus, but even more closely related (within the subfamily velociraptorinae, see Classification, below). A specimen of Velociraptor has been found with quill knobs on the ulna. Quill knobs are where the follicular ligaments attached, and are a direct indicator of feathers of modern aspect.
vs
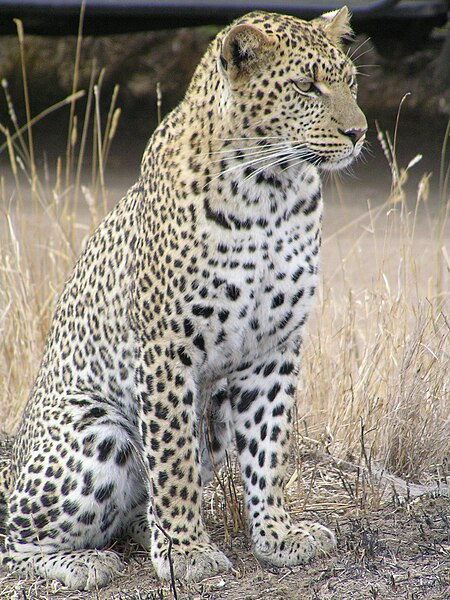

Leopards are agile and stealthy predators. Although smaller than other members of the Panthera genus, they are able to take large prey due to their massive skulls that facilitate powerful jaw muscles. Head and body length is between 95 and 165 cm (37 and 65 in), and the tail reaches 60 to 110 cm (24 to 43 in). Shoulder height is 45 to 80 cm (18 to 31 in). The muscles attached to the scapula are exceptionally strong, which enhance their ability to climb trees. They are very diverse in size. Males are about 30% larger than females, weighing 30 to 91 kg (66 to 200 lb) compared to 23 to 60 kg (51 to 130 lb) for females. Large males of up to 91 kg (200 lb) have been documented in Kruger National Park in South Africa; however, males in the South Africa's coastal mountains average 31 kg (68 lb) and the females from the desert-edge in Somalia average 23 to 27 kg (51 to 60 lb). This wide variation in size is thought to result from the quality and availability of prey found in each habitat. The most diminutive leopard subspecies overall is the Arabian leopard (P. p. nimr), from deserts of the Middle East, with adult females of this race weighing as little as 20 kg (44 lb). Other large subspecies, in which the males can also weigh up to 91 kg (200 lb), are the Sri Lankan leopard (P. p. kotiya) and the rare, little-known Anatolian leopard (P. p. tulliana). The largest verified leopard weighed 96.5 kg (213 lb), with larger sizes reported but considered unreliable. The leopard's body is comparatively long, and its legs are short.